Urology: A critical Field in Modern Medical care
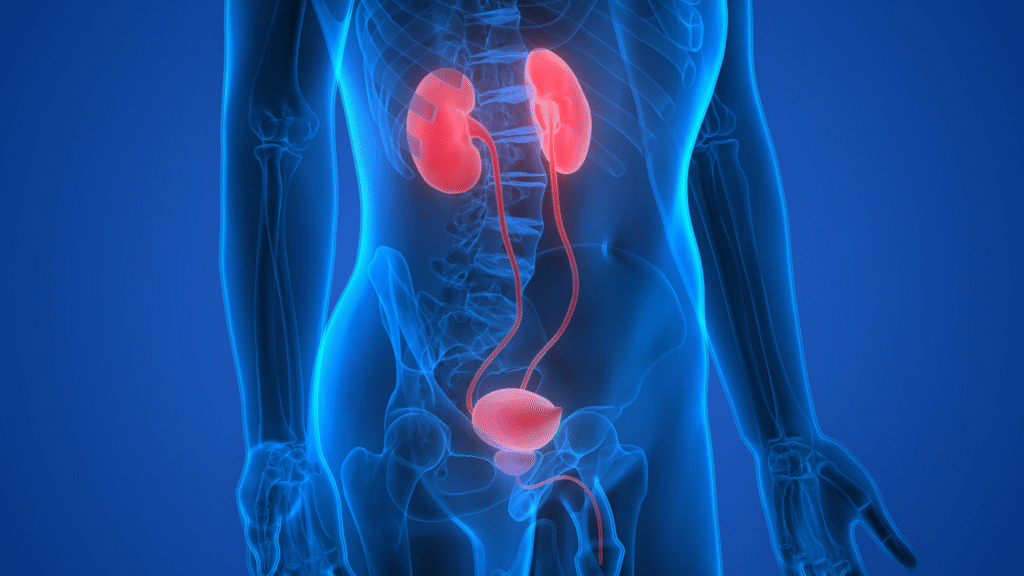
Urology is a vital branch of medicine that deals with the diseases and conditions affecting the urinary tract and the male reproductive organs. This includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra, and, in men, the prostate and testes. Urologists diagnose urology clinic and treat a wide variety of issues such as urinary tract infections, kidney stones, bladder control problems, prostate enlargement, and cancers of the urinary system. Their work is essential to ensuring proper waste elimination from the body and maintaining reproductive health. Urology combines surgical and non-surgical treatments, making it a dynamic and diverse medical specialty that plays a central role in patient care across age groups and genders.
One of the most common urological conditions is kidney stones, which occur when mineral deposits form in the kidneys and pass painfully through the urinary tract. These stones can cause severe discomfort and may lead to infections or kidney damage if not treated promptly. Another prevalent issue is urinary incontinence, especially among older adults and women who have undergone childbirth. This condition can be socially and emotionally distressing, but urologists can offer effective treatments including pelvic floor therapy, medications, or surgery. Diagnosis in urology often involves imaging studies, urine analysis, blood tests, and procedures like cystoscopy to examine the bladder.
Urology also addresses significant male reproductive health concerns. Prostate problems are a major area of focus, particularly as men age. Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), or prostate enlargement, can lead to difficulty urinating and frequent urges, disrupting daily life. Prostate cancer, one of the most common cancers in men, requires early detection for the best outcome, and urologists play a crucial role in screening and treatment. They use tools like prostate-specific antigen (PSA) tests, biopsies, and advanced imaging to diagnose and manage prostate diseases. Treatments vary from medications to radiation therapy, minimally invasive procedures, and in some cases, surgical removal of the prostate.
Female urology is another important subspecialty that deals with conditions unique to the female urinary system. Women often face bladder issues such as overactive bladder, interstitial cystitis, and urinary tract infections, which can be recurrent and significantly affect quality of life. Childbirth and menopause are major contributing factors to these problems, leading to weakened pelvic muscles and hormonal changes. Urologists work closely with gynecologists in managing these issues, offering therapies ranging from medications and bladder training exercises to surgical procedures like sling operations for incontinence. Increasing awareness and better diagnostic tools have led to more women seeking urological care.
Children are also affected by urological disorders, and pediatric urology focuses on diagnosing and treating problems like undescended testicles, congenital urinary tract abnormalities, bedwetting, and urinary tract infections in infants and young children. Early intervention is crucial to prevent long-term kidney damage and ensure proper development. Pediatric urologists often use non-invasive imaging and gentle surgical techniques to manage these conditions. Education for parents and ongoing monitoring are key aspects of pediatric urological care, which aims to support the child’s health and development while minimizing anxiety and discomfort.
Recent advancements in urology have greatly enhanced patient outcomes. The introduction of minimally invasive surgical techniques, such as laparoscopy and robotic-assisted surgery, has reduced recovery times and surgical risks. Urologists now have access to more precise imaging and diagnostic tools, enabling earlier and more accurate detection of diseases. Telemedicine has also expanded access to urological care, particularly in remote areas. As public awareness of urological health grows, more individuals are seeking preventive care and timely treatment. Urology continues to be a cornerstone of comprehensive medical practice, supporting critical bodily functions and improving quality of life through dedicated and specialized care.
Leave a Comment